Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to create new tables in the PostgreSQL database using Python.
This tutorial picks up from where the Connecting to PostgreSQL database server tutorial left off.
Steps for creating tables in PostgreSQL from Python
To create a new table in a PostgreSQL database, you use the following steps:
- First, connect to the PostgreSQL server by calling the
connect()function. Theconnect()function returns aconnectionobject. - Second, create a
cursorobject by calling thecursor()method of theconnectionobject. - Third, execute the
CREATE TABLEby calling theexecute()method of thecursorobject. - Finally, close the connection.
If you use the with statement, you don’t need to explicitly close the connection.
Creating tables in Python example
Let’s take an example of creating tables from Python.
1) Create a Python program
First, create a new file in the project directory called create_tables.py.
Second, define a new function called create_tables() in the create_tables.py module:
import psycopg2
from config import load_config
def create_tables():
""" Create tables in the PostgreSQL database"""
commands = (
"""
CREATE TABLE vendors (
vendor_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
vendor_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL
)
""",
""" CREATE TABLE parts (
part_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
part_name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL
)
""",
"""
CREATE TABLE part_drawings (
part_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
file_extension VARCHAR(5) NOT NULL,
drawing_data BYTEA NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (part_id)
REFERENCES parts (part_id)
ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE CASCADE
)
""",
"""
CREATE TABLE vendor_parts (
vendor_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
part_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (vendor_id , part_id),
FOREIGN KEY (vendor_id)
REFERENCES vendors (vendor_id)
ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE CASCADE,
FOREIGN KEY (part_id)
REFERENCES parts (part_id)
ON UPDATE CASCADE ON DELETE CASCADE
)
""")
try:
config = load_config()
with psycopg2.connect(**config) as conn:
with conn.cursor() as cur:
# execute the CREATE TABLE statement
for command in commands:
cur.execute(command)
except (psycopg2.DatabaseError, Exception) as error:
print(error)
if __name__ == '__main__':
create_tables()How it works.
First, initialize a list of CREATE TABLE statements:
commands = ...Next, read the connection parameters using the load_config() function of the config module:
config = load_config()Then, connect to the PostgreSQL server using the connect() function of the psycopg2 module. The connect() function returns a connection object:
with psycopg2.connect(**config) as conn:The with statement will close the database connection automatically.
After that, create a new cursor object from the connection object using the cursor() function:
with conn.cursor() as cur:The with statement will also automatically close the cursor once it is no longer in use.
Finally, iterate over the command in the commands list and execute each of them using the execute() method:
for command in commands:
cur.execute(command)The create_tables() function will create four tables in the suppliers database:
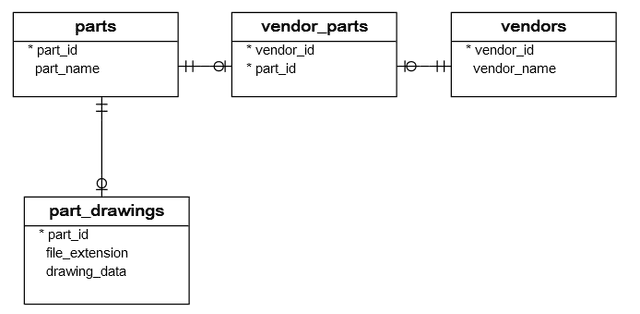
vendors– stores vendor data.parts– stores the part data.vendor_parts– stores the links between vendors and parts.part_drawings– stores the drawing of the parts.
The following diagram illustrates the tables and their relationships:
2) Execute the create_tables.py script
The following command executes the create_tables.py module that calls the create_tables() function:
python create_table.py3) Verify the table creation
First, open the Command Prompt on Windows or Terminal on Unix-like systems and connect to the PostgreSQL server using the psql client tool.
psql -U postgresIt’ll prompt you for a password for the postgres user.
Second, change the current database to suppliers:
\c suppliersThird, show tables in the suppliers database using the \dt command:
\dtOutput:
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner
--------+---------------+-------+----------
public | part_drawings | table | postgres
public | parts | table | postgres
public | vendor_parts | table | postgres
public | vendors | table | postgres
(4 rows)The output indicates that the suppliers database has four tables.
Download the project source code
Summary
- Call the
execute()method of theCursorobject to execute aCREATE TABLEstatement to create a new table in the database.