Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the PostgreSQL NTH_VALUE() function to get a value from the nth row in a result set.
Introduction to PostgreSQL NTH_VALUE() function
The NTH_VALUE() function returns a value from the nth row in an ordered partition of a result set.
Here is the syntax of the NTH_VALUE() function:
NTH_VALUE(expression, offset)
OVER (
[PARTITION BY partition_expression]
[ ORDER BY sort_expression [ASC | DESC]
frame_clause ]
)Let’s examine the syntax of the NTH_VALUE() function in detail.
expression
The expression is the target column or expression on which the NTH_VALUE() function operates.
offset
The offset is a positive integer (greater than zero) that determines the row number relative to the first row in the window against which the expression evaluates.
PARTITION BY partition_expression
The PARTITION BY clause distributes rows of the result set into partitions to which the NTH_VALUE() function applies.
ORDER BY sort_expression
The ORDER BY clause sorts rows in each partition to which the function is applied.
frame clause
The frame_clause defines the subset (or the frame) of the current partition.
PostgreSQL NTH_VALUE() function examples
We will use the products table created in the window functions tutorial for the demonstration.
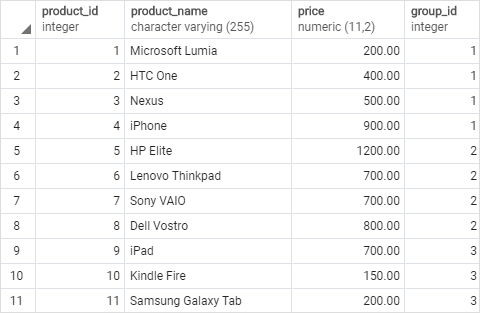
1) Using PostgreSQL NTH_VALUE() function over the result set example
This example uses the NTH_VALUE() function to return all products together with the second most expensive product:
SELECT
product_id,
product_name,
price,
NTH_VALUE(product_name, 2)
OVER(
ORDER BY price DESC
RANGE BETWEEN
UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND
UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING
)
FROM
products;Here is the output:
 In this example:
In this example:
- The
ORDER BYclause sorted all products by prices from high to low - The frame clause defined the frame start at the beginning row and end at the ending row of the result set.
- The
NTH_VALUE()function return value in the product_name column of the second row of the result set after sorting and framing.
2) Using PostgreSQL NTH_VALUE() function over a partition example
This example uses the NTH_VALUE() function to return all products with the second most expensive product for each product group:
SELECT
product_id,
product_name,
price,
group_id,
NTH_VALUE(product_name, 2)
OVER(
PARTITION BY group_id
ORDER BY price DESC
RANGE BETWEEN
UNBOUNDED PRECEDING AND
UNBOUNDED FOLLOWING
)
FROM
products;The following picture illustrates the output:
 In this example,
In this example,
- The
PARTITION BYclause to distributed products into product groups (or partitions) specified by the values in thegroup_idcolumn. - The
ORDER BYclause sorted the products in each product group from high to low. - The frame clause defined the whole partition as a frame.
- And the
NTH_VALUE()function returns the product name of the 2nd row of each product group.
Now, you should how to use the PostgreSQL NTH_VALUE() function to get a value from the nth row of a result set.