Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the PostgreSQL EXCEPT operator to return a result set containing the rows in the first query that does not appear in the output of the second query.
Introduction to the PostgreSQL EXCEPT operator
Like the UNION and INTERSECT operators, the EXCEPT operator returns rows by comparing the result sets of two or more queries.
The EXCEPT operator returns distinct rows from the first (left) query that are not in the second (right) query.
The following illustrates the syntax of the EXCEPT operator.
SELECT select_list
FROM A
EXCEPT
SELECT select_list
FROM B;The queries that involve the EXCEPT need to follow these rules:
- The number of columns and their orders must be the same in the two queries.
- The data types of the respective columns must be compatible.
The following Venn diagram illustrates the EXCEPT operator:
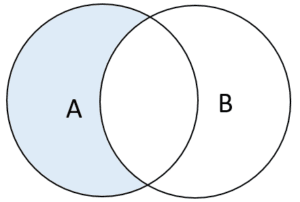 If you want to sort the rows in the combined result sets, you need to place the
If you want to sort the rows in the combined result sets, you need to place the ORDER BY clause after the second query:
SELECT select_list
FROM A
EXCEPT
SELECT select_list
FROM B
ORDER BY sort_expression;Setting up sample tables
We’ll create the top_rated_films and most_popular_films tables for demonstration:
CREATE TABLE top_rated_films(
title VARCHAR NOT NULL,
release_year SMALLINT
);
CREATE TABLE most_popular_films(
title VARCHAR NOT NULL,
release_year SMALLINT
);
INSERT INTO top_rated_films(title, release_year)
VALUES
('The Shawshank Redemption', 1994),
('The Godfather', 1972),
('The Dark Knight', 2008),
('12 Angry Men', 1957);
INSERT INTO most_popular_films(title, release_year)
VALUES
('An American Pickle', 2020),
('The Godfather', 1972),
('The Dark Knight', 2008),
('Greyhound', 2020);
SELECT * FROM top_rated_films;
SELECT * FROM most_popular_films;The contents of the top_rated_films table:
title | release_year
--------------------------+--------------
The Shawshank Redemption | 1994
The Godfather | 1972
The Dark Knight | 2008
12 Angry Men | 1957
(4 rows)The contents of the most_popular_films table:
title | release_year
--------------------+--------------
An American Pickle | 2020
The Godfather | 1972
The Dark Knight | 2008
Greyhound | 2020
(4 rows)PostgreSQL EXCEPT operator examples
Let’s take some examples of using the EXCEPT operator
1) Basic EXCEPT operator example
The following statement uses the EXCEPT operator to find the top-rated films that are not popular:
SELECT * FROM top_rated_films
EXCEPT
SELECT * FROM most_popular_films;Output:
title | release_year
--------------------------+--------------
The Shawshank Redemption | 1994
12 Angry Men | 1957
(2 rows)2) Using the EXCEPT operator with the ORDER BY clause
The following statement uses the ORDER BY clause in the query to sort the result set returned by the EXCEPT operator by titles:
SELECT * FROM top_rated_films
EXCEPT
SELECT * FROM most_popular_films
ORDER BY title;Output:
title | release_year
--------------------------+--------------
12 Angry Men | 1957
The Shawshank Redemption | 1994
(2 rows)Notice that we placed the ORDER BY clause after the second query to sort the films by titles.
Summary
- Use the PostgreSQL
EXCEPToperator to combine rows from two result sets and return a result set containing rows from the first result set that do not appear in the second result set.