Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn about various kinds of PostgreSQL joins including inner join, left join, right join, and full outer join.
PostgreSQL join is used to combine columns from one (self-join) or more tables based on the values of the common columns between related tables. The common columns are typically the primary key columns of the first table and the foreign key columns of the second table.
PostgreSQL supports inner join, left join, right join, full outer join, cross join, natural join, and a special kind of join called self-join.
Setting up sample tables
Suppose you have two tables called basket_a and basket_b that store fruits:
CREATE TABLE basket_a (
a INT PRIMARY KEY,
fruit_a VARCHAR (100) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE basket_b (
b INT PRIMARY KEY,
fruit_b VARCHAR (100) NOT NULL
);
INSERT INTO basket_a (a, fruit_a)
VALUES
(1, 'Apple'),
(2, 'Orange'),
(3, 'Banana'),
(4, 'Cucumber');
INSERT INTO basket_b (b, fruit_b)
VALUES
(1, 'Orange'),
(2, 'Apple'),
(3, 'Watermelon'),
(4, 'Pear');The tables have some common fruits such as apple and orange.
The following statement returns data from the basket_a table:
SELECT * FROM basket_a;Output:
a | fruit_a
---+----------
1 | Apple
2 | Orange
3 | Banana
4 | Cucumber
(4 rows)The following statement returns data from the basket_b table:
SELECT * FROM basket_b;Output:
b | fruit_b
---+------------
1 | Orange
2 | Apple
3 | Watermelon
4 | Pear
(4 rows)PostgreSQL inner join
The following statement joins the first table (basket_a) with the second table (basket_b) by matching the values in the fruit_a and fruit_b columns:
SELECT
a,
fruit_a,
b,
fruit_b
FROM
basket_a
INNER JOIN basket_b
ON fruit_a = fruit_b;Output:
a | fruit_a | b | fruit_b
---+---------+---+---------
1 | Apple | 2 | Apple
2 | Orange | 1 | Orange
(2 rows)The inner join examines each row in the first table (basket_a). It compares the value in the fruit_a column with the value in the fruit_b column of each row in the second table (basket_b). If these values are equal, the inner join creates a new row that contains columns from both tables and adds this new row to the result set.
The following Venn diagram illustrates the inner join:
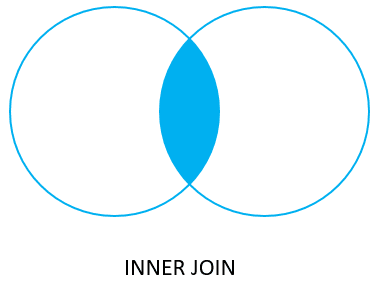
PostgreSQL left join
The following statement uses the left join clause to join the basket_a table with the basket_b table. In the left join context, the first table is called the left table and the second table is called the right table.
SELECT
a,
fruit_a,
b,
fruit_b
FROM
basket_a
LEFT JOIN basket_b
ON fruit_a = fruit_b;Output:
a | fruit_a | b | fruit_b
---+----------+------+---------
1 | Apple | 2 | Apple
2 | Orange | 1 | Orange
3 | Banana | null | null
4 | Cucumber | null | null
(4 rows)The left join starts selecting data from the left table. It compares values in the fruit_a column with the values in the fruit_b column in the basket_b table.
If these values are equal, the left join creates a new row that contains columns of both tables and adds this new row to the result set. (see the row #1 and #2 in the result set).
In case the values do not equal, the left join also creates a new row that contains columns from both tables and adds it to the result set. However, it fills the columns of the right table (basket_b) with null. (see the row #3 and #4 in the result set).
The following Venn diagram illustrates the left join:
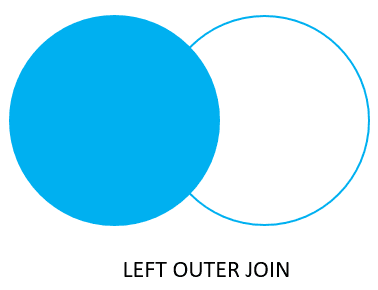 To select rows from the left table that do not have matching rows in the right table, you use the left join with a
To select rows from the left table that do not have matching rows in the right table, you use the left join with a WHERE clause. For example:
SELECT
a,
fruit_a,
b,
fruit_b
FROM
basket_a
LEFT JOIN basket_b
ON fruit_a = fruit_b
WHERE b IS NULL;The output is:
a | fruit_a | b | fruit_b
---+----------+------+---------
3 | Banana | null | null
4 | Cucumber | null | null
(2 rows)Note that the LEFT JOIN is the same as the LEFT OUTER JOIN so you can use them interchangeably.
The following Venn diagram illustrates the left join that returns rows from the left table that do not have matching rows from the right table:

PostgreSQL right join
The right join is a reversed version of the left join. The right join starts selecting data from the right table. It compares each value in the fruit_b column of every row in the right table with each value in the fruit_a column of every row in the fruit_a table.
If these values are equal, the right join creates a new row that contains columns from both tables.
In case these values are not equal, the right join also creates a new row that contains columns from both tables. However, it fills the columns in the left table with NULL.
The following statement uses the right join to join the basket_a table with the basket_b table:
SELECT
a,
fruit_a,
b,
fruit_b
FROM
basket_a
RIGHT JOIN basket_b ON fruit_a = fruit_b;Here is the output:
a | fruit_a | b | fruit_b
------+---------+---+------------
2 | Orange | 1 | Orange
1 | Apple | 2 | Apple
null | null | 3 | Watermelon
null | null | 4 | Pear
(4 rows)The following Venn diagram illustrates the right join:
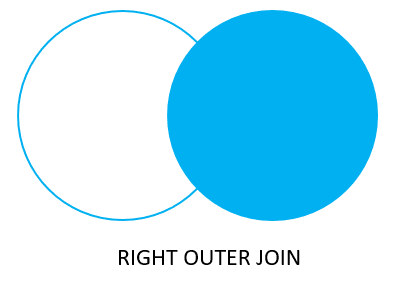 Similarly, you can get rows from the right table that do not have matching rows from the left table by adding a
Similarly, you can get rows from the right table that do not have matching rows from the left table by adding a WHERE clause as follows:
SELECT
a,
fruit_a,
b,
fruit_b
FROM
basket_a
RIGHT JOIN basket_b
ON fruit_a = fruit_b
WHERE a IS NULL;Output:
a | fruit_a | b | fruit_b
------+---------+---+------------
null | null | 3 | Watermelon
null | null | 4 | Pear
(2 rows)The RIGHT JOIN and RIGHT OUTER JOIN are the same therefore you can use them interchangeably.
The following Venn diagram illustrates the right join that returns rows from the right table that do not have matching rows in the left table:

PostgreSQL full outer join
The full outer join or full join returns a result set that contains all rows from both left and right tables, with the matching rows from both sides if available. In case there is no match, the columns of the table will be filled with NULL.
SELECT
a,
fruit_a,
b,
fruit_b
FROM
basket_a
FULL OUTER JOIN basket_b
ON fruit_a = fruit_b;Output:
a | fruit_a | b | fruit_b
------+----------+------+------------
1 | Apple | 2 | Apple
2 | Orange | 1 | Orange
3 | Banana | null | null
4 | Cucumber | null | null
null | null | 3 | Watermelon
null | null | 4 | Pear
(6 rows)The following Venn diagram illustrates the full outer join:
 To return rows in a table that do not have matching rows in the other, you use the full join with a
To return rows in a table that do not have matching rows in the other, you use the full join with a WHERE clause like this:
SELECT
a,
fruit_a,
b,
fruit_b
FROM
basket_a
FULL JOIN basket_b
ON fruit_a = fruit_b
WHERE a IS NULL OR b IS NULL;Here is the result:
a | fruit_a | b | fruit_b
------+----------+------+------------
3 | Banana | null | null
4 | Cucumber | null | null
null | null | 3 | Watermelon
null | null | 4 | Pear
(4 rows)The following Venn diagram illustrates the full outer join that returns rows from a table that do not have the corresponding rows in the other table:
 The following picture shows all the PostgreSQL joins that we discussed so far with the detailed syntax:
The following picture shows all the PostgreSQL joins that we discussed so far with the detailed syntax:
 In this tutorial, you have learned how to use various kinds of PostgreSQL joins to combine data from multiple related tables.
In this tutorial, you have learned how to use various kinds of PostgreSQL joins to combine data from multiple related tables.